flagyl injection uses
- Dr Maheen Zaiba
- Apr 20, 2025
- 6 min read
فلیگائل انجیکشن کا استعمال
Written by Dr Maheen Zaiba [PharmD, DOW University Of Health Sciences (DUHS)], Karachi, Pakistan)
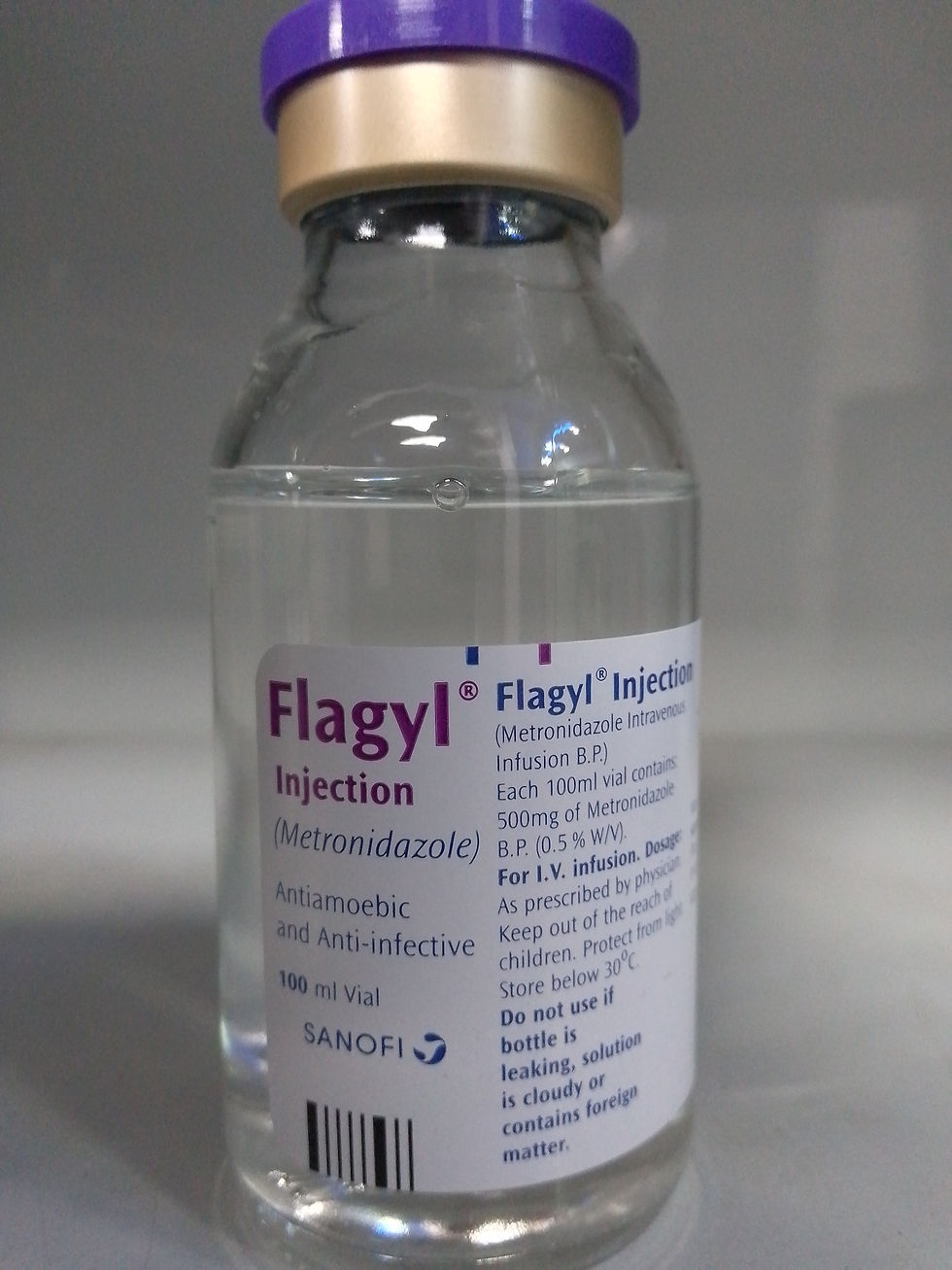
Brand name:
Flagyl
Generic name:
Metronidazole
Available dosage forms and their doses:
Capsule
· 375mg
Tablet
· 250mg
· 500mg
Tablet, extended-release
· 750mg
Oral suspension
· 500mg/5ml
Infusion solution
· 500mg/100ml
Price:
190.61 Rs per vial
Therapeutic class:
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole used to treat trichomoniasis, amebiasis, inflammatory lesions of rosacea, and bacterial infections, as well as prevent postoperative infections. (
Antimicrobial & antiprotazoal)
Pharmacological class:
Nitroimidazole class of antibiotics.
Manufacturer:
Sanofi Aventis
Storage:
Oral tablets. Metronidazole oral tablets should be stored at room temperature, between 68 f to 77 f(20 c to 25 c). Store in a cool, dry place. Protect from light.
Oral capsules. Metronidazole oral capsules should be stored at room temperature, between 59 f to 77 f (15 c to 25 c).
Oral liquid. Metronidazole oral liquid should be stored at room temperature, between 68 f to 77 f(20 c to 25 c). Store in a cool, dry place. Do not freeze it. Throw away any medicine left in the bottle ten days after opening it.
Prescription drug:
Yes
Mechanism of action:
Metronidazole diffuses into the organism, inhibits protein synthesis by interacting with dna,
And causes a loss of helical dna structure and strand breakage. Therefore, it causes cell death in susceptible organisms. The mechanism of action of metronidazole occurs through a four-step process.
Indications & dosages:
Anaerobic bacterial infections
Loading dose: 15 mg/kg iv; not to exceed 4 g/day
Maintenance dose: 7.5 mg/kg po/iv (over 1 h) q6hr x 7-10 days (or 2-3 weeks if severe)
Oral suspension
· 7.5 mg/kg po q8hr for 7-10 days; not exceed a 4 g/24 hr
· infections of the bone and joint, lower respiratory tract, and endocardium may require longer treatment
Sexually transmitted disease
Prevention following sexual assault
2 g po as a single dose; 3-drug regimen that also includes ceftriaxone or cefixime, plus
Azithromycin or doxycycline (cdc std guidelines, 2010)
Bacterial vaginosis
Nonpregnant women
· 500 mg po bid x 7 days, or
· 2 g po qday single dose, or
· extended-release: 750 mg po qday x 7 days
Pregnant women
· 500 mg po bid x 7 days, or
· 250 mg po tid x 7 days
Colorectal surgical infection
Prophylaxis; start after mechanical bowel preparation the afternoon and evening before surgery 1 g po q6-8hr for 3 doses 15 mg/kg iv over 30-60 min; complete approximately 1 hr before surgery; may administer 7.5 Mg/kg iv over 30-60 min at 6 and 12 hr after initial dose for maintenance; discontinue within 12 Hr after surgery
Trichomoniasis
250 mg po q8hr for 7 days 2 g po qday single dose; alternatively, 1g po q12hr for 2 doses
Individualize dosage regimen
· single-dose treatment may help improve compliance, especially if administered under
Supervision, in those patients who may be nonadherent to a seven-day regimen
· seven-day treatment may minimize reinfection by protecting patient long enough for
Sexual contacts to obtain appropriate treatment; some data suggest cure rates may be higher
After a seven-day course of treatment than after a one-day treatment regimen;
· if a repeat course of therapy is required, a 4- to 6-weeks need to elapse between courses
And reconfirmed presence of the trichomonad; monitor total and differential leukocyte
Counts before and after re-treatment
Amebiasis
Acute intestinal amebiasis (acute amebic dysentery): 750 mg po tid 5-10 days
Amebic liver abscess:
500-750 mg po tid for 5-10 days
Giardiasis (non-fda use)
500 mg po q12hr for 5-7 days
Gardnerella infection
Immediate release: 500 mg po q12hr
Extended-release: 750 mg po qday for 7 days; take on empty stomach
Helicobacter pylori infection (off-label)
250-500 mg po qid in combination with tetracycline (500 mg) and bismuth subsalicylate (525
Mg) x 14 days
Nongonococcal urethritis (off-label)
2 g po qday single dose with erythromycin (500 mg qid) or erythromycin ethylsuccinate (800
Mg qid) x 7 days
Pelvic inflammatory disease (off-label)
500 mg po q12hr for 14 days in conjunction with ofloxacin or levofloxacin
Dosage modifications
Renal impairment
· mild-to-moderate: Dose adjustment not considered necessary as elimination half-life not
Significantly altered
· severe or end-stage renal disease: Metronidazole and metronidazole metabolites may
Accumulate significantly because of reduced urinary excretion; monitor patients not
Undergoing hemodialysis
· hemodialysis removes significant amounts of metronidazole and its metabolites from
Systemic circulation; supplementation may be necessary
· peritoneal dialysis: Monitor for signs of toxicity due to potential accumulation of
Metronidazole metabolites
Hepatic impairment
· mild-to- moderate (child-pugh a or b): No dosage adjustment necessary; monitor
· severe (child-pugh c): Reduce dose of by 50%
Dosing considerations
Hepatic failure
· mild to moderate hapatic impairment (child-pugh a or b): No dosage adjustment needed
But patients should be monitored for metronidazole associated adverse events
· severe hepatic impairment: Reduce dose of by 50%
Renal failure
· mild to moderate renal impairment: Dose adjustment not considered necessary as
Elimination half-life not significantly altered
· severe renal impairment or end stage of renal disease: Metronidazole and metronidazole
Metabolites may accumulate significantly because of reduced urinary excretion; monitor in
Severe renal impairment or end stage of renal disease, not undergoing hemodialysis
· hemodialysis removes significant amounts of metronidazole and its metabolites from
Systemic circulation; supplementation may be necessary
· peritoneal dialysis: Monitor for signs of toxicity due to potential accumulation of
Metronidazole metabolites
Crohn disease (orphan)
Topical treatment of active perianal crohn disease
Side effects:
· allergic reactions—skin rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or
Throat
· dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, confusion or trouble speaking
· fever, neck pain or stiffness, sensitivity to light, headache, nausea, vomiting,
Confusion
· heart rhythm changes—fast or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, feeling faint or
Lightheaded, chest pain, trouble breathing
· liver injury—right upper belly pain, loss of appetite, nausea, light-colored stool,
Dark yellow or brown urine, yellowing skin or eyes, unusual weakness or fatigue
· pain, tingling, or numbness in the hands or feet
· redness, blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin, including inside the mouth
· seizures
· severe diarrhea, fever
· sudden eye pain or change in vision such as blurry vision, seeing halos around
Lights, vision loss
· unusual vaginal discharge, itching, or odor
Common side effects:
· diarrhea
· metallic taste in mouth
· nausea
· stomach pain
Interactions:
· disulfiram: Avoid taking this medication if you have been on therapy with disulfiram
Within the last 14 days. Concomitant administration can lead to serious side effects that
Require medical attention.
· alfuzosin.
· amiodarone.
· amisulpride.
· bupropion.
· chlorpromazine.
· ciprofloxacin.
· clarithromycin.
· clomipramine.
· desipramine.
· donepezil.
· erythromycin.
· felbamate.
· fluconazole.
· fluorouracil.
· fluoxetin.
· fosphenytoin.
· gemifloxacin.
· haloperidol.
· levofloxacin.
· moxifloxacin.
· olanzapine.
· probucol.
· quetiapine.
· quinidine.
· sotalol.
· warfarin.
These are some of the significant interacting drugs with metronidazole. Contact the physician or Pharmacist to check for interactions before taking the drug with other drugs.
With alcohol: The combination of metronidazole with alcohol may cause nausea, vomiting,
Rapid heartbeat, and facial flushing. While using metronidazole and for at least three days
Following the last dose, avoid alcohol completely.
With diseases:
· liver diseases: Dose adjustment may be required.
· kidney diseases: Delayed elimination of drug reported. It may require dose adjustment.
· low blood counts: Taking this medication may worsen these signs
· cockayne syndrome: A rare genetic disorder.
Pregnancy & lactation:
Flagyl (metronidazole) is generally not recommended during the first trimester of pregnancy due To potential risks, but it can be used later in pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks. It's also not recommended during breastfeeding because it can pass into breast milk and may affect the baby.
Fda pregnancy category b - no proven risk in humans.
Precautions:
· dermatologic: Topical cream use may cause skin irritation.
· metabolic: Caution is advised if on current therapy with corticosteroid drugs, those on a
Controlled sodium diet, or those predisposed to edema (swelling of face, limbs, etc.).
· liver problems: Dose needs to be adjusted.
· kidney diseases: Kidney diseases can slow down the excretion of the medication. So,
Dose adjustments may be required.
· low blood cell counts: Metronidazole may cause low blood counts. Hence, inform the
Doctor if the blood counts are low.
· pregnancy: Pregnant women with trichomoniasis vaginalis, regardless of
The pregnancy stage, should be tested and assessed by their physician before starting the
Medication.
Do not use mteronidazole in the following conditions:
A known allergy to the medication or any of its components.
Concomitant administration with alcohol or products containing propylene glycol.
Administration of drug disulfiram with or within two weeks.
Cockayne syndrome (a genetic condition characterized by small head size, stature, and slow
Development).
First trimester (1 to12 week) of pregnancy.
Warnings
Black box warnings
Potenial for carcinogenicity
· metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice and rats
· avoid unnecessary use
· reserve for use in trichomoniasis and anaerobic bacterial infection.
Counselling points:
· tablets: Swallow the medication as a whole after food.
· liquid: Measure the right dose using a syringe or measure and take each dose, preferably
After food.
· suppository: Follow the instructions given on the package.
· gel and cream: Apply on the affected area and rub gently, as directed by the doctor.
Missed dose:
Take this medication as soon as you remember if a dose is missed. If the next dose is near, skip the missed one and take the regular dosing regimen. Do not take two or double doses together.
Overdose:
In case of overdosing on the medication, contact the emergency department or the nearest poison control center immediately.



Comments