nezkil syrup uses
- Dr. Taha Murtaza

- Mar 30, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Apr 5, 2025
Written by Dr Taha Murtaza [PharmD, DOW University Of Health Sciences (DUHS)], Karachi, Pakistan)
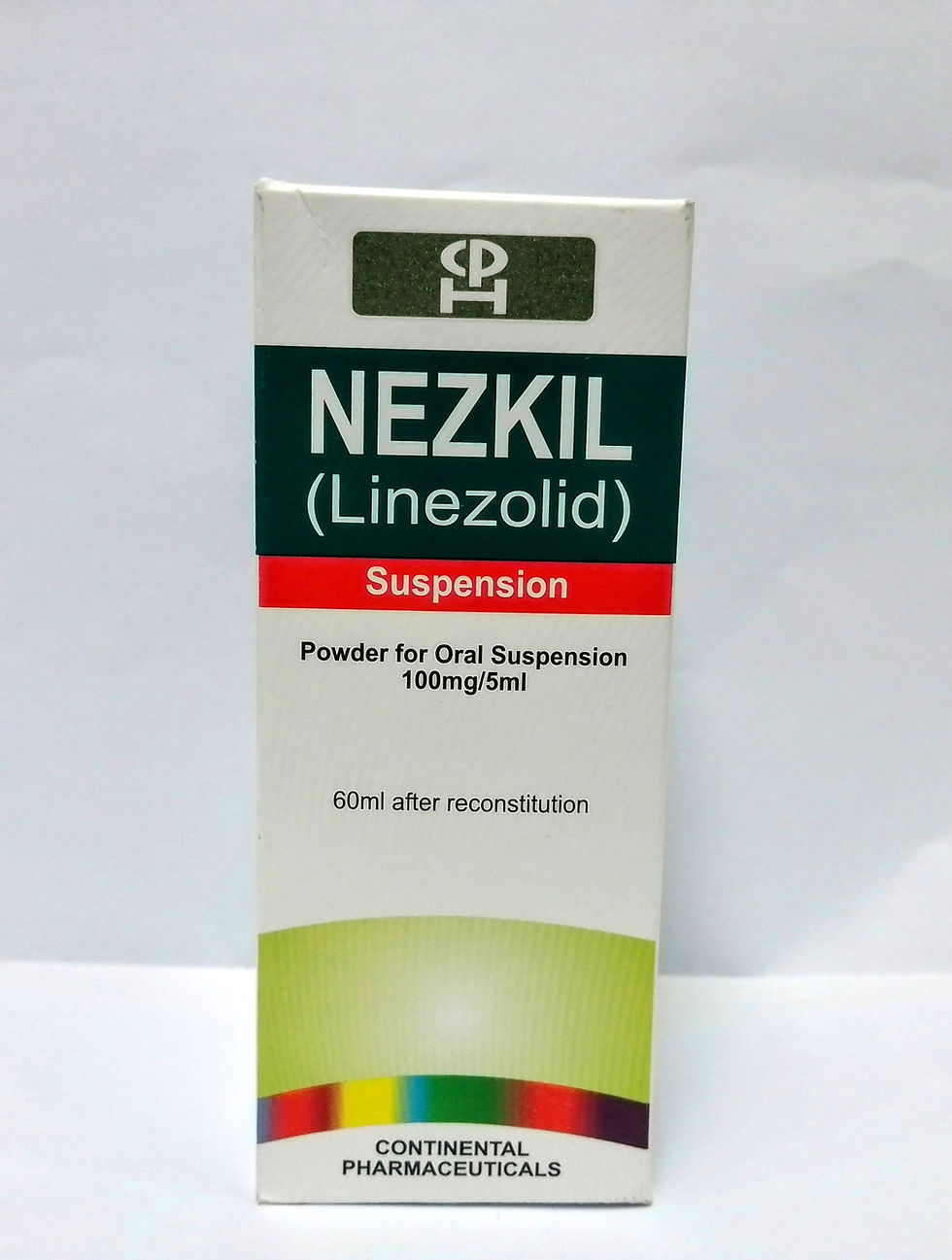
Generic:
Linezolid
Manufacturer:
Continental Pharmaceuticals
Prescription drug?
Yes
Avaialable dosage forms:
Nezkil 600mg infusion: Each 300ml contains linezolid.....600mg
Nezkil 200mg infusion: Each 100ml contains linezolid.....200mg
Nezkil 600mg tablet: Each tablet contains linezolid.....600mg
Nezkil 400mg tablet: Each tablet contains linezolid.....400mg
Nezkil suspensipn: Each 5ml contains linezolid.....400mg
Pharmacological class:
Protein synthesis inhibitor (50s-protein subunit inhibitor)
Therapeutic class:
Antibiotic
Chemistry:
Synthetic compound belongs to the oxazolidinone class
Indication: Vancomycin-resistant enterococcus faecium infections, including cases with concurrent bacteremia.
Dose and route of administration:
Paeds (birth-11years):
10mg/kg IV/PO q8h.
Adults:
600mg IV/PO q12 h
Recommended duration of treatment (consecutive days):
14 to 28
Indication: Nosocomial pneumonia caused by staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and resistant strains) or streptococcus pneumonia (including multi-drug resistant strains)
Dose:
Paeds: (Birth-11years):
10mg/kg IV/PO q8h.
Adult (12 years older)
600mg IV/PO q12h
Recommended duration of treatment (consecutive days):
10 to 14 days.
Indication: Complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and resistant strains), streptococcus pyogenes, or Streptococcus agalactia.
Dose:
Paeds: (Birth-11years)
10mg/kg IV/PO q8h.
Adult (12 years older)
600mg IV/PO q12h
Recommended duration of treatment (consecutive days): 10 to 14 days.
Indication: Uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and resistant strains).
Dose:
Paeds: (birth-11years age)
< 5 years: 10mg/kg PO q8h
5-11 years: 10mg/kg PO q12h
Adolescents:
600mg PO q12h
Adults: 400mg PO q12h
Recommended duration of treatment (consecutive days):
10 to 14 days
Community-acquired pneumonia caused by streptococcus pneumonia (including multi-drug resistant strains) including cases with concurrent bacteremia or staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains only)
Dose:
Paeds: (Birth-11years)
10mg/kg IV/PO q8h.
Adult (12 years older)
600mg IV/PO q12h
Recommended duration of treatment (consecutive days):
10 to 14 days.
Special population:
Geriatrics:
No dose adjustment is required.
Gender:
The same dose is used in males and females.
Renal insufficiency:
No dose adjustment is required.
Hepatic insufficiency:
In patients with child-pugh class A or B i.e. mild-moderate hepatic dysfunction, no dose adjustment is required but patients with severe hepatic dysfunction, pharmacokinetics have not been evaluated.
Pregnancy:
FDA has called linezolid a category C antibiotic for the use in pregnant women means it can only be used by pregnant mothers in case where emergency is required i.e. benefits surpasses side effects.
Lactation:
If alternate antibiotic is available, then kindly refused this in lactating mothers.
Contra-indications:
In patients with hypersensitivity to linezolid or any of the components of the product.
Side-effects:
Common:
Diarrhea
Headache
Nausea
Others:
Vomiting
insomnia
Constipation
rash
Dizziness
fever
oral moniliasis
vaginal moniliasis
hypertension
dyspepsia
localized abdominal pain
pruritis
tongue discoloration
Precautions:
Patients with pseudomembranous colitis should avoid linezolid
The superinfection produced by clostridium difficle should be managed during treatment with linezolid.
Thrombocytopenia could occur, and platelets of patients should be monitored.
Interactions:
With Mono-amino-oxidase inhibitors
With adrenergic agents
With serotonergic agents.




Comments